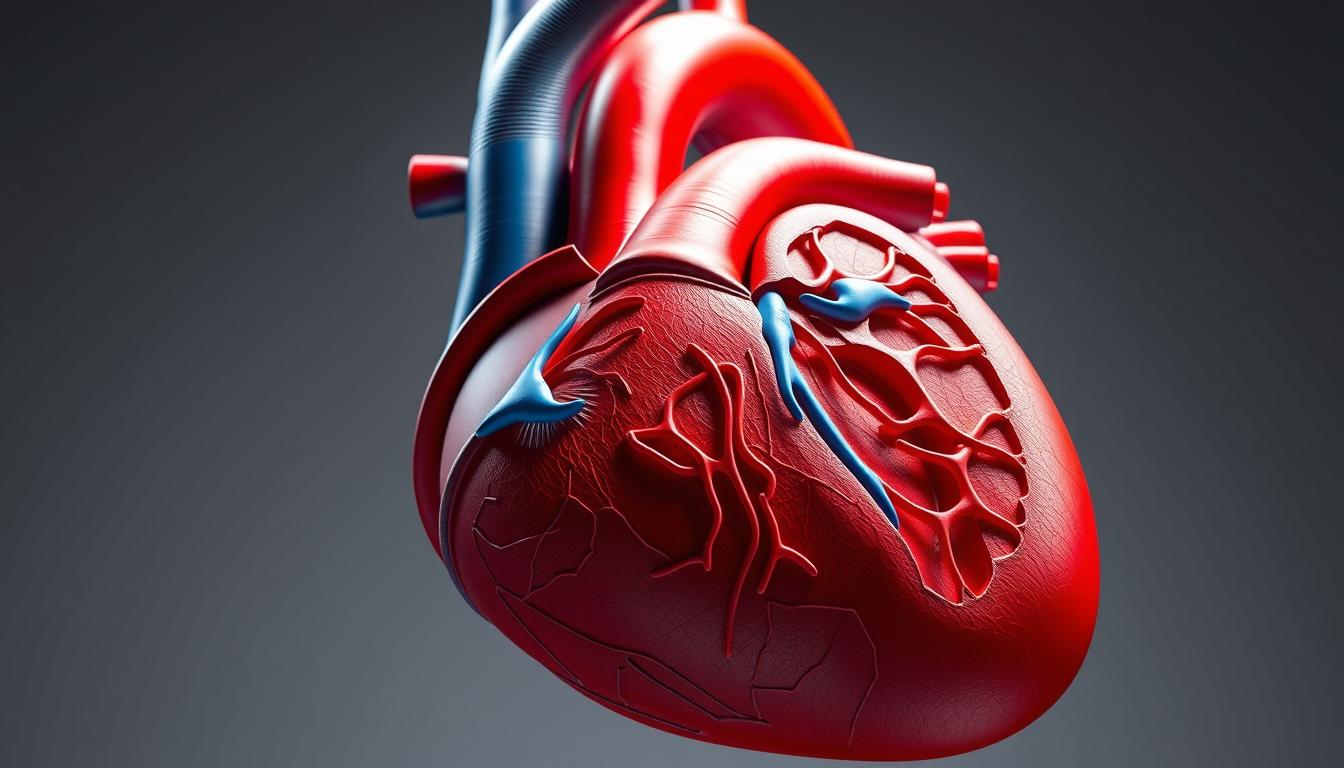
Octopuses are truly fascinating creatures. They have three hearts, which are key to their anatomy. These marine animals have a complex body that helps them live well underwater. Their unique features are quite interesting.

In this article, we’ll explore the amazing anatomy of octopuses. We’ll focus on their three hearts and how they help their bodies work. We’ll also look at the benefits of having multiple hearts. This makes them stand out in the sea.
Key Takeaways
- Octopuses have three hearts that contribute to their overall physiology
- Their complex anatomy allows them to thrive in their underwater environment
- Octopuses are a unique part of marine life with fascinating characteristics
- Their three hearts play a crucial role in their octopus anatomy
- Having multiple hearts provides several benefits and advantages to octopuses
- Understanding the anatomy of octopuses can provide insights into their behavior and survival
The Fascinating World of Octopus Anatomy
Octopuses have a unique body plan. They have a large head, eight arms, and a mantle. Their anatomy is adapted for life underwater, with features like gills and a radula. Their heart structure is just one of the many fascinating aspects of octopus anatomy.
In the field of marine biology, octopuses are a favorite to study. They can change color, texture, and shape. This is thanks to their skin cells and muscles. Some key features of octopus anatomy include:
- A large head with a highly developed brain
- Eight arms covered with suckers, which are used for crawling, swimming, and grasping
- A mantle that houses the octopus’s internal organs, including its heart structure
These features make octopuses well-suited to their underwater home. The study of octopus anatomy is key in marine biology. It helps us understand how these creatures evolved and developed.
Why Octopuses Have Three Hearts
Octopuses have a special cardiovascular system with three hearts. Two hearts, called branchial hearts, pump blood to the gills. The third heart, the systemic heart, sends blood to the rest of the body. This setup is crucial for their marine physiology and helps them pump blood efficiently.
The three hearts work together to keep the octopus healthy. The branchial hearts send blood to the gills for oxygen. Meanwhile, the systemic heart pumps blood to the rest of the body. This system supports their high metabolism and active lifestyle. The octopus hearts are also very efficient, helping them save energy and live in different water environments.
- Three hearts that work together to pump blood to the entire body
- Branchial hearts that pump blood to the gills for oxygen extraction
- A systemic heart that pumps blood to the rest of the body
These features help the octopus thrive in water. It makes them one of the most interesting creatures, with a unique marine physiology that meets their needs.
How the Three-Heart System Works
An octopus has a special circulatory system that is both complex and efficient. It has three hearts that work together to keep blood flowing to its body. This system is key for oxygenating the octopus and keeping it healthy.
The blood circulation in an octopus is quite interesting. The systemic heart pumps blood to the body. Meanwhile, the branchial hearts send blood to the gills for oxygen. This ensures the octopus gets the oxygen and nutrients it needs to survive.
- Efficient oxygenation of the blood
- Regulated blood flow to the body
- Complex network of blood vessels
This system makes the octopus’s circulatory system very effective. It shows how well the octopus can adapt and survive in different conditions.
The Blue Blood Phenomenon
Octopuses have a unique trait: their blue blood. This color comes from copper-based hemocyanin, which carries oxygen. This is key for octopuses to survive in cold, oxygen-poor places.
In marine biochemistry, this blood is crucial. It helps octopuses live well underwater. The hemocyanin molecule binds to oxygen, then releases it to the body’s tissues. This is vital for the octopus’s survival, helping it save energy and stay healthy.
Some key aspects of the blue blood phenomenon include:
- Copper-based hemocyanin: the molecule responsible for oxygen transport
- Efficient oxygen transport: allows the octopus to thrive in low-oxygen environments
- Marine biochemistry: the study of the chemical processes that occur in marine organisms
Studying blue blood helps us understand marine biochemistry and octopus adaptations. By looking at copper-based hemocyanin, scientists learn about octopuses’ complex physiology.
Evolutionary Advantages of Multiple Hearts
Octopuses have three hearts, which gives them many benefits. These benefits help them live well in deep-sea environments. One big advantage is that they can pump blood more efficiently. This is key because deep-sea environments often have very little oxygen.
The three hearts of octopuses are very important for their survival. They help octopuses adapt to different places. Over time, octopuses have evolved to live in many different environments. This has helped them survive and even thrive in places where others might not make it.
- Increased survival rates in low-oxygen environments
- Improved ability to hunt and capture prey in deep-sea environments
- Enhanced ecological competitiveness, allowing octopuses to coexist with other marine species
Compared to other sea creatures, octopuses have a very special heart system. This system lets them survive in places where others would struggle. Their hearts are a result of long-term evolution, making them unique in the sea.
Heart Function During Different Activities
The hearts of octopuses are very adaptable. They are key to their cardiac function. When octopuses swim, rest, or hunt, their hearts work differently. For example, when swimming, their hearts pump blood faster to meet the oxygen demand.
This shows how exercise physiology works in octopuses.
Learning about octopus heart function in various activities helps us understand their marine behavior. Here are some important points:
- During swimming, the hearts of octopuses pump blood more rapidly to meet the increased oxygen demand.
- When an octopus is at rest, its heart rate slows down, and energy conservation becomes a priority.
- During hunting behavior, the hearts of octopuses are more alert and responsive to prey, allowing for rapid reaction times.
In conclusion, octopus hearts are very adaptable. They are crucial for their cardiac function in different activities. By studying octopus heart function, we can appreciate their unique marine behavior and the role of exercise physiology in their lives.
The Connection Between Hearts and Intelligence
Research shows that octopuses’ hearts are key to their neural control and cognitive function. This link between hearts and smarts in octopuses has caught the eye of scientists. They’re eager to learn more about how it affects marine cognition.
Octopuses’ hearts are linked to their brain power. Studies indicate that their heart system helps manage neural activity. This connection is intriguing, offering insights into marine cognition.
Some important facts about octopuses’ hearts and smarts include:
- Their heart system helps control neural control and cognitive function
- Octopuses have a special heart design for better blood flow and brain oxygen
- Octopuses with better heart systems often solve problems more effectively
The bond between octopuses’ hearts and their intelligence is complex and captivating. It holds many secrets for understanding marine cognition and neural control. More research is needed to grasp this relationship fully.
Common Misconceptions About Octopus Hearts
Octopus anatomy is full of fascinating facts, but myths are common too. Their heart system is often misunderstood. In marine science, it’s key to know the truth and debunk myths to understand these creatures better.
Recent studies have revealed the truth about octopus hearts. They show that octopuses have three hearts, each with a special role. This contradicts the popular myth of a single heart.
Debunking Popular Myths
Many think octopus hearts are not efficient or prone to failure. But research proves they are very efficient and can pump blood well, even in cold water. By looking at scientific facts and debunking myths, we learn more about these amazing animals and their role in marine science.
Recent Research Findings
New research has improved our understanding of octopus heart anatomy and function. It shows that octopuses have a special heart system for their gills. This helps them even when oxygen is scarce. This knowledge is important for marine science and understanding these fascinating creatures.
Conclusion: Understanding These Remarkable Creatures
Exploring the octopus anatomy and the secrets of marine biology shows us how amazing these creatures are. Their unique three-heart system and other special features make them stand out. By learning about their biology, we can help protect them and their homes in the ocean.
Octopuses have complex brains and solve problems in clever ways. Their intelligence is unmatched by many sea creatures. As we keep studying them, we learn more about the world around us. There’s still so much to discover about these incredible animals.
The octopus’s body is a marvel of nature’s diversity and ability to adapt. By being curious and protecting these creatures, we ensure future generations can also be amazed by their biology.
FAQ
What is the purpose of octopuses having three hearts?
Octopuses have three hearts to keep blood and oxygen flowing. Two hearts pump blood to the gills. The third heart sends blood to the rest of the body.
How does the three-heart system of octopuses work?
The three hearts work together to circulate blood and oxygen. The systemic heart pumps blood to the body. The branchial hearts pump blood to the gills for oxygen. This system helps octopuses live well underwater.
Why is the blood of octopuses blue?
Octopuses have blue blood because of copper-based hemocyanin. This molecule carries oxygen to their tissues. It’s an adaptation for efficient oxygen use underwater.
What are the evolutionary advantages of having multiple hearts?
Octopuses’ three hearts offer several benefits. They help in survival, adapting to deep-sea life, and competing in their ecosystem. The multiple hearts ensure efficient blood and oxygen delivery.
How do the hearts of octopuses function during different activities?
Octopuses’ hearts adjust based on activity. When swimming, they pump blood faster for more oxygen. At rest, they slow down to save energy. Their hearts also aid in hunting, with quicker responses to prey.
What is the connection between the hearts and intelligence of octopuses?
There’s a link between octopuses’ hearts and their intelligence. Their cardiovascular system affects their brain function. This suggests their unique anatomy may boost their intelligence and problem-solving skills.
What are some common misconceptions about octopus hearts?
Many believe octopuses have only one heart or that their hearts are inefficient. But research has debunked these myths. It has given us a better understanding of their complex heart anatomy and function.